Coastal resilience means building the ability of a community to “bounce back” after hazardous events such as hurricanes, coastal storms, and flooding – rather than simply reacting to impacts
Coastal areas are exposed to a number of hazards including sudden onset hazards such as tsunami and storm surges, and
slow onset hazards such as sea level rise due to climate change. Supporting the resilience of communities in coastal areas
in facing these threats and challenges requires an in-depth understanding of their natural and demographic
characteristics and analysis of the actual and potential trends that should inform development planning and decision-making processes.
This Coastal Resilience Toolkit was developed under the regional engagement component of the Australia-Indonesia
The partnership with the Disaster Risk Management Program (SIAP SIAGA) aims to support decision-makers in conducting technical
analyses and designing collaborative approaches that will mitigate disaster-related threats and enhance the resilience of
coastal areas and their residents.
The Coastal Resilience Toolkit (CRT) is a relatively simple-to-use set of procedures, packaged within a software-based
toolkit which aims to support governments in coastal areas to attain sustainable coastal resilience for populations at
risk of threats emanating from their location next to the sea.
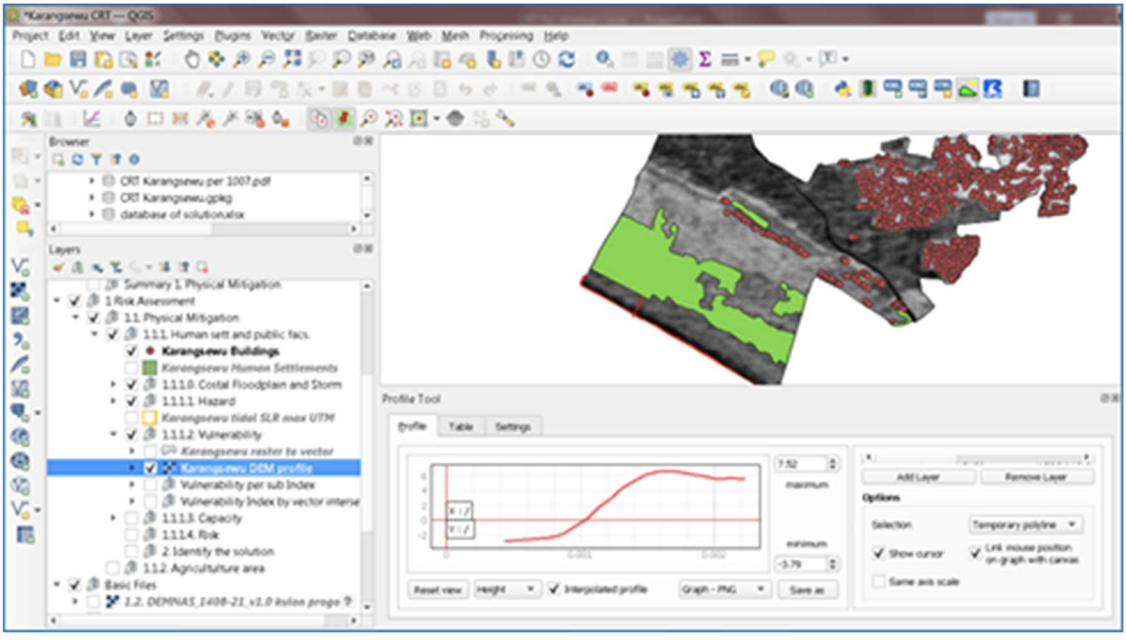
The CRT operates on a platform based on QGIS software, a desktop geographic information system application that
supports viewing, editing, reporting, and analysis of geospatial data. Its ability to analyse and visualise digital information
makes it a state-of-the-art tool to enable a data-supported approach to the development of coastal resilience mapping
and related mitigation efforts. The CRT works in complementarity with and relies upon additional inputs such as the
outcomes of discussion forums, the provision of information from resource persons, expert judgment, and other
analytical tools outside QGIS capabilities.
The CRT also provides a solutions database which is based on documented best practices from Indonesia and Australia in
responding to various coastal hazards (abrasion, extreme sea waves, tsunami) and damage types (human settlements,
agriculture, mangrove, coral reef, etc). These solutions are either nature-based or a combination of hard structures (such
as sea walls, and wave breakers) and soft structures (e.g. mangroves), are environmentally friendly, cost-effective, include
a strong community involvement element, and are integrated with other aspects of development, particularly economics.
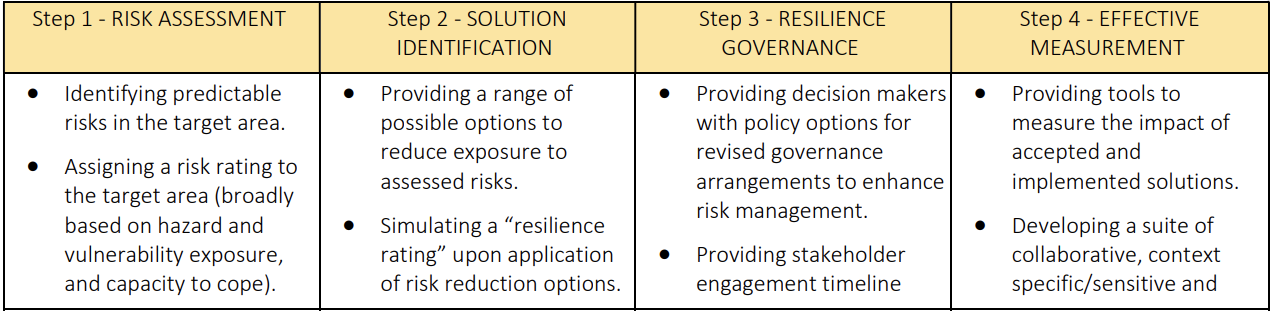
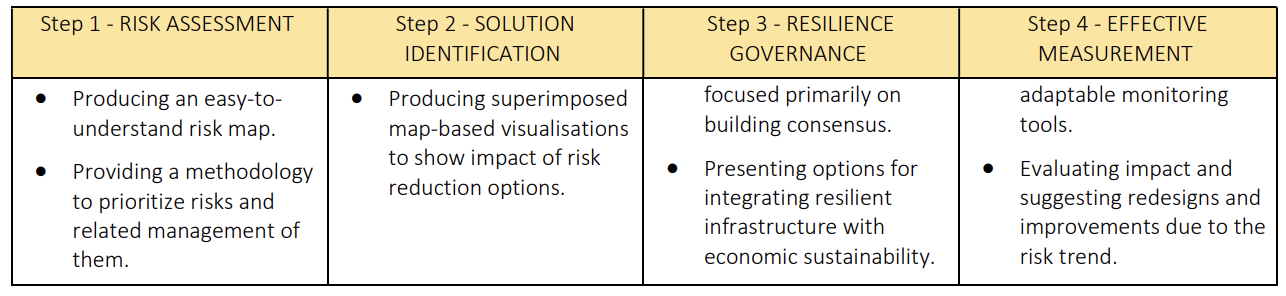
TECHNICAL FEATURES
As QGIS is a free and open-source software hence the CRT and all its features are free and can be modified according to
the local demand. The CRT can be accessed via BNPB website (web address and contact person to be confirmed) and
provides several technical features